In our latest article, concerning TATA CALF mixers, we mentioned the Agriculture 4.0 System. We therefore want to address, as promised, the topic of Industry 4.0, so as to clarify what it is, how it is identified and what innovations it has brought to the production sectors.
We will also see the previous three industrial revolutions, identifying the fundamental aspects and technological innovations of each.
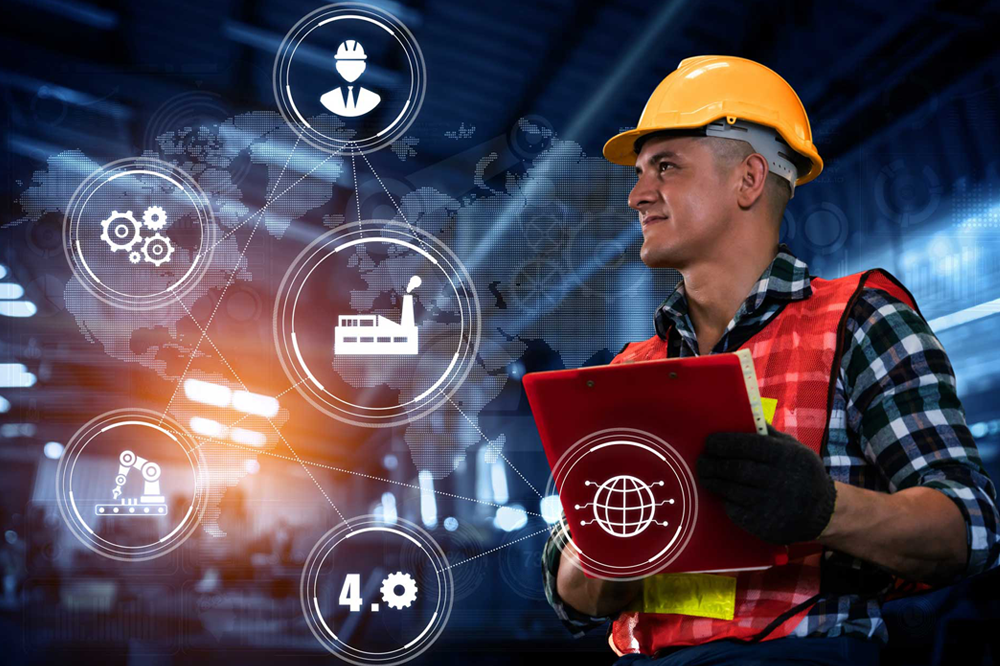
What is Industry 4.0?
The term Industry 4.0 identifies the fourth industrial revolution. This revolution, compared to the previous ones, has as its protagonist an enabling technology, placed inside the machinery or production and work plant.
It’s nothing more than a solution or a technological improvement that contains many research and development activities, able to reinvigorate the production system by exploiting fast, clear, direct and precise interconnection processes between company assets.
By connecting all assets, the availability of all information in real time benefits production. Productivity, speed, immediate control, product competitiveness, but above all growth in production efficiency are the strengths of this new industrial revolution.
The first industrial revolution
Before arriving at this last industrial revolution, the fourth identified in history, there were three more. What are the three previous industrial revolutions? How are they identified? How did they affect production and industrial development?
We will analyze them all, starting from the first in chronological order. The first industrial revolution dates back to the late eighteenth century, when machinery was driven by mechanical energy, with the use of coal to develop steam as an energy power. Britain first came to industrial expansion, in the mid-1700s, and was the first to spread some technical innovations that distinguish a turning point in European and world industrialization.
This rapid development also contributed to the expansion and sharp increase in agricultural production, thanks to new cultivation and breeding techniques. Productive innovation was also useful in improving living conditions, mitigating famines.
It was a real agricultural innovation; with the new techniques developed the land never remains unproductive, doubles the fertility of the soil and allows the breeding of a large amount of livestock. Industry 1.0 is ultimately the set of changes in the production of manufactured goods that has resulted in a decisive turnaround in consumption, lifestyle and social relations.
The second industrial revolution
The second industrial revolution began in the early 1900s. Electric current took the place of coal and steam engines, the bulb, wireless telegraph, bicycle, automobile and even electric motors were invented. New artificial substances have been created, such as fertilizers, which lead to increased agricultural production, and disinfectants that improve living conditions. Among the new metal alloys that are made, there is aluminum that with plastic allows the creation of machinery for storing food, refrigerators.
During the Second Industrial Revolution, milk pasteurization and antibiotics were also born, while in the mechanical field gasoline, the internal combustion engine, the diesel engine and the typewriter. Industry 2.0 integrates scientific research, industry and technology. This industrial development radically transforms agriculture, industrial overproduction is intertwined with the agrarian crisis.
The third industrial revolution
The third industrial revolution began in the late 1980s and has continued to this day; electronics further automates production. The microprocessor is born and with it the computers. The third industrial revolution is called the computer revolution and can be compared to the industrial revolution of the late nineteenth century. The railways reduced the distances, while the internet will totally cancel them out.
Old industries are totally reinvented, computer science, biotechnology, robotics and microelectronics are born. Research, innovation and technology are the new strength of agricultural machinery and livestock equipment. An evolved economy needs advanced agriculture. Agriculture produces energy and brings it to the forefront of future development strategies.
The development of agriculture
Since the early 1900s, agriculture has experienced incredible development. At the beginning of the last century there was a high rate of labor with low productivity, while already in 1950 there was a sharp increase in agricultural mechanization, with the use of chemical and plant protection fertilizers. Due to a sharp increase in the garments present in farms, in 1950 the first herringbone milking parlors were introduced, greatly improving productivity and milking time.
In 1970 electronics were introduced to milking systems and in the 1990s the first automatic milking system was introduced to the market. The system of geolocation and monitoring of the yield of the agricultural machine and also of the milking system was introduced.
What does 4.0 mean?
The fourth industrial revolution, namely Industry 4.0 and Agriculture 4.0, allows the real-time connection between technology and operator. Access to the necessary data is possible through a simple smartphone, instantly analyzing the data and information collected. Agriculture and zoo-technical farming become precision, production processes are digitized, the efficiency and effectiveness of production are greatly improved.
Agriculture 4.0
In agriculture 4.0 the water needs of a given culture can be determined and calculated, thus avoiding water waste. Diseases can be predicted in plants or pests that could drastically ruin a crop can be detected in advance. Agriculture 4.0 allows traceability of the supply chain, allowing the control of the processing during each step of the same. Digital innovation 4.0 makes it possible to produce high-quality food, minimizing the margin of error.